DeFi
Executive Summary: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a rapidly growing subset of the cryptocurrency ecosystem that creates financial applications and services that operate on decentralized, open blockchain networks. Borrowing and lending have rapidly become some of the most-used DeFi applications.
Despite some troubles in crypto lending during the summer of 2022, DeFi lending continues to attract interest, with institutions pouring billions into the sector. Improvements to DeFi lending protocols and regulatory clarity will bring greater adoption, making this an interesting space for investors.
What is DeFi Lending?
DeFi lending is about offering crypto loans on decentralized platforms through peer-to-peer decentralized applications (dapps). In DeFi lending, users can lend their cryptocurrency assets to other users in exchange for interest, or borrow cryptocurrency assets by posting collateral to reduce the risk of default.
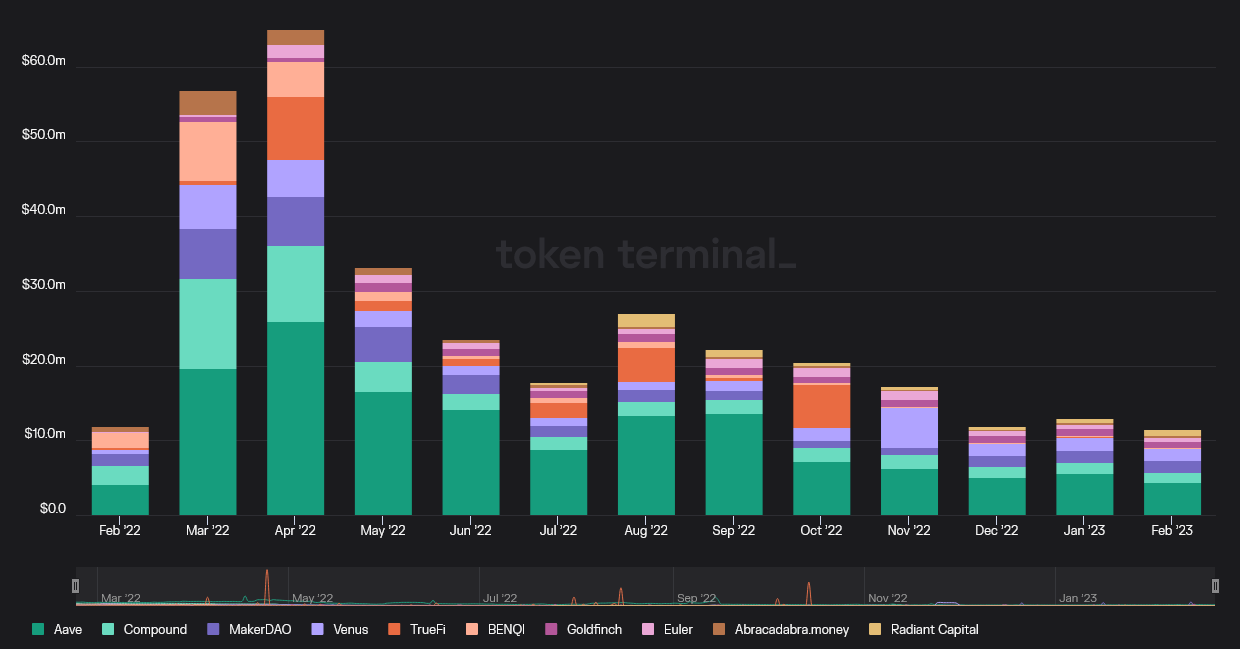
Among dapps, DeFi lending has the highest growth rate globally. According to Zion Market Research, the global DeFi market was valued at nearly $11.96 billion in 2021, and is expected to reach $232.20 billion by 2030.

While Total Value Locked (TVL) in DeFi lending platforms is trending upward as of this writing, it still has some way to go to recover from its pre-crash levels of $45 billion from April 2022. (The crypto market moves in tandem.)
Some of the encouraging developments in the crypto space are the rise of bitcoin Ordinals, the growth of liquid staking tokens, and the upcoming Ethereum Shanghai upgrade.
The primary risk factor is the SEC crypto crackdown, which has specifically targeted lending platforms (among others). So far, DeFi lending platforms appear to be safer bets, as it’s not clear who the SEC could sue, if there technically is no company.
How DeFi Lending Works
Like a traditional banking loan facility that relies on customer deposits to lend out money, DeFi lending mainly relies on lending pools where users deposit their crypto assets to ensure quick distribution among borrowers through smart contracts.
One of the key advantages of DeFi lending and borrowing platforms is they are open and transparent. Anyone with an internet connection and a cryptocurrency wallet can participate, and the code that governs these platforms is often open-source, meaning that anyone can audit it to ensure that it is secure and fair.
It is also possible to see all the deposits, loans, and repayments made by examining the blockchain ledger. Additionally, because there is no centralized intermediary, users do not have to go through the lengthy and cumbersome process of credit checks.
Instead, borrowers typically have to put up more collateral than the amount they’re borrowing. Collateralization rates typically range between 120% and 150% on major lending platforms. Why put down 1.5 ETH to borrow 1ETH, you ask? Because there is no credit check. We can trust the borrower, because we’ve already got her money.
Overcollateralizing also allows a cushion if the price of the underlying crypto drops unexpectedly.
Platforms also have a “liquidation ratio” relative to the borrowed amount. For instance, a 100% collateralization rate could be accompanied by an 80% liquidation ratio. If the collateral falls below this rate, anyone can liquidate the amount minus the lender’s deposit and pocket the rest. For this reason, many borrowers lock up even more than the required collateral.
DeFi lending is primarily used to leverage bigger trades, i.e., to buy and trade even more crypto. For this reason, taking out DeFi loans is dangerous to your wealth. Serving as a lender, however, can be profitable.
Investment Thesis
There are two ways to invest in most lending platforms: acting as a lender, or buying and holding the platform token.
Acting as a lender: Investors who deposit their crypto assets into these DeFi protocols receive lending tokens in return (aTokens for Aave, cTokens for Compound, and Dai for MakerDAO). Think of these like “receipts.”
These lending tokens are embedded with both the interest and principal, and can be redeemed at any time. The exchange rate between the crypto asset and the native coins is called the annual percentage yield (APY): this is how the lenders make money. And the interest rate is determined by the ratio between the supplied and borrowed tokens in a particular market.
Buying and holding the platform token: Most DeFi lending platforms have their own token (AAVE for Aave, COMP for Compound, and MKR for MakerDAO). In our view, buying and holding these platform tokens is the long-term investment opportunity.
At Bitcoin Market Journal, we believe that holding the native tokens of promising crypto projects is like owning “stock” in the “company.” We buy and hold great projects earning real revenue, run by capable leaders, with good long-term growth prospects.
Reasons to be long-term bullish on DeFi lending:
- Because DeFi lending takes place on a blockchain, all transactions are recorded on a public ledger, which can be viewed and audited by anyone. This transparency helps to prevent fraud.
- DeFi lending platforms are automated (no credit checks needed), so they’re more cost-efficient and speedy.
- The process is totally digital. Hence analytics is easy as the open data gives an insight into the borrowing and lending market.
- DeFi lending protocols allow interoperability and programmability.
- Some investors maximize savings by investing in different lending platforms, then depositing the lending tokens in interest-bearing accounts.
Reasons to be wary of DeFi lending:
- Regulators have their sights on lending services, and could find a way to shut down DeFi lending as well (or choke its access to TradFi banks).
- Because they have to be overcollateralized, they’re not really loans for people who need them.
- Smart contract risk: the lending platforms are at risk of being targeted by hackers looking to exploit bugs.
- Considering the volatility of crypto markets, overcollateralization and liquidation are continuous risks for users. The collapse of Terra/Luna and FTX are cases in point. Borrowers are vulnerable to losing all their crypto, if the price drops suddenly.
- Users need to be extra cautious with wallets and addresses. Losing your private key means that your funds are lost forever: there are no regulations to cover such losses.
- DeFi loans can encourage bad behavior: loaning out crypto to buy more crypto, repeatedly, building a dangerous Jenga tower of risk:

Top DeFi Lending Platforms
 Aave (AAVE) is an open-source, non-custodial, decentralized protocol for lending and borrowing cryptocurrency. Users deposit their digital assets to earn interest or borrow assets with customizable interest rates. Aave has some innovative features, such as flash loans that have to be paid back within a single Ethereum block (~12 seconds).
Aave (AAVE) is an open-source, non-custodial, decentralized protocol for lending and borrowing cryptocurrency. Users deposit their digital assets to earn interest or borrow assets with customizable interest rates. Aave has some innovative features, such as flash loans that have to be paid back within a single Ethereum block (~12 seconds).
Aave Arc is a liquidity pool specifically designed for institutions. Unlike the retail Aave platform, which requires no KYC, the Arc platform includes KYC requirements to maintain regulatory compliance.
Several institutional investors have invested in Aave. Grayscale has a DeFi fund, with AAVE forming over 12% of the portfolio. Aave has a 14% presence in Bitwise’s DeFi Crypto index fund.
At the time of writing, Aave has a significant Twitter following of over 522.8K, a Reddit community with over 16,000 subscribers, 15k telegram followers, and 22k Discord members.
 Compound (COMP) allows users to earn interest or borrow assets using their crypto as collateral. It operates on the automated market maker (AMM) model and enables seamless transactions between lenders and borrowers. COMP is an ERC-20 native token and is also the governance token for the protocol.
Compound (COMP) allows users to earn interest or borrow assets using their crypto as collateral. It operates on the automated market maker (AMM) model and enables seamless transactions between lenders and borrowers. COMP is an ERC-20 native token and is also the governance token for the protocol.
Compound has been widely recognized as a pioneer in the DeFi space and has attracted a large and active community. Compound has over 242,000 followers on Twitter, a Reddit community with over 45,000 subscribers, and a Discord channel with over 19,000 members.
Compound has become a popular choice for users with its user-friendly interface and transparent governance. Compound Finance is the 6th largest dapp and the 3rd largest lending protocol in the DeFi space.
 MakerDAO (MKR) enables users to borrow DAI, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, using their cryptocurrency holdings as collateral. MKR token holders govern the Maker protocol.
MakerDAO (MKR) enables users to borrow DAI, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, using their cryptocurrency holdings as collateral. MKR token holders govern the Maker protocol.
As DeFi continues to mature, MakerDAO is well-positioned to play a significant role in the space and provide users with access to stable, decentralized lending and borrowing options.
MakerDAO has over 240,000 followers on Twitter, a Reddit community with over 34,000 subscribers, and a Discord channel with over 7,000 members.
 Alchemix (ALCX) is an interesting take on DeFi, offering loans that pay themselves off through yield-generating strategies.
Alchemix (ALCX) is an interesting take on DeFi, offering loans that pay themselves off through yield-generating strategies.
Alchemix allows users to deposit tokens and then take loans against those tokens, at a 1:2 ratio. The deposited tokens are put into Yearn vaults to earn yield, and that yield is used to pay down the loans. Currently users can use ETH, WSTETH, RETH, DAI, USDT, or USDC as collateral for the loans.
Alchemix is not as active on social media as some other DeFi projects, and boasts just 72,800 Twitter followers, 10,000 members on its Discord channel, and 1,100 members of its subreddit.
 C.R.E.A.M Finance (CREAM) is a decentralized lending protocol for accessing financial services with a goal of pushing the boundaries of what DeFi can do.
C.R.E.A.M Finance (CREAM) is a decentralized lending protocol for accessing financial services with a goal of pushing the boundaries of what DeFi can do.
C.R.E.A.M is an acronym for “Crypto Rules Everything Around Me.” It is a part of the yearn.finance ecosystem and is a permissionless, open-source and blockchain-agnostic protocol serving users on Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon and Fantom.
Users who are holding ETH or wBTC can deposit their assets on C.R.E.A.M. to earn yield, similar to a traditional savings account. On Twitter, the protocol has 80,500 followers, and on the subreddit there are just 329 members.
DeFi Institutional Investments
The volatility in the crypto market has not dissuaded investors from their continued interest in DeFi projects. A recent survey found 20% to 50% of crypto-related pitches were focused on DeFi. Decentralized money markets issue billions of dollars in loans, while DeFi platforms like Uniswap trade volumes roughly 30% those of Coinbase.
Institutional interest in DeFi is rising, too:
- Banks are beginning to venture into crypto custody firms.
- Barclay’s bought a stake in Copper.
- Standard Chartered has partnered with Northern Trust to launch Zodia, a cryptocurrency custodian for institutional investors.
- Bank of New York Mellon has partnered with Chainalysis to track and analyze cryptocurrency products.
- BlackRock and Citigroup invested over $1 billion each in DeFi platforms in 2022.
- Recently, Nomura’s subsidiary Laser announced its investment in Infinity, a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol for institutional lending and borrowing.
Investor Takeaway
If DeFi lending wants to be a part of the “real” economy, it needs to expand beyond crypto assets and tokenize real-world assets, while relying less on collateral. Over-reliance on crypto collateral means that dapps are accessible only to asset-rich borrowers, limiting the financial inclusion benefits.
Though institutional crypto investment is increasing, DeFi’s progress going forward will largely hinge on regulatory outcomes. In June, the World Economic Forum released a policy toolkit for fair and efficient DeFi regulations. And in the U.S., the Stablecoin TRUST Act has the potential to make stablecoins fully regulated and accepted as a part of the traditional financial system.
Anyone looking into DeFi now should know that it is still very early times for the sector, with the potential for great risks, and even greater rewards.
Subscribe to our Bitcoin Market Journal newsletter to keep in touch with investing opportunities in the DeFi sector.


