- 1 Uniswap V3 allows to work in bounded ranges lesser than (0,∞)
- 2 It provides UNI governance in addition to design different fee structures
- 3 In Uniswap V3, it is possible to create multiple pools for each pair of token that too with different swap fees
An advanced version to Uniswap V1 and Uniswap V2, Uniswap V3 is Automated Market Maker (AMM) which gives liquidity providers higher control over price ranges in which the capital deposited by them is used without significantly affecting liquidity fragmentation and gas efficiency.
Uniswap V3 also works on the similar constant product [x*y=k] with added features. These are:
Concentrated Liquidity: The ability to concentrate liquidity by bounding it within an arbitrary price range is given to liquidity providers. In previous versions, liquidity was distributed along the reserve curve [x*y=k] where, x and y are reserves of the assets X and Y respectively while k is a constant. With the earlier version, liquidity was provided across the entire price range (0, ∞) while with V3 liquidity is provided across the smaller (finite) range than (0, ∞). Liquidity concentrated in a finite range known as Position. A position only needs to maintain liquidity reserve to facilitate trade between this range and therefore acts like constant product pools within larger reserves called virtual reserves within the range.
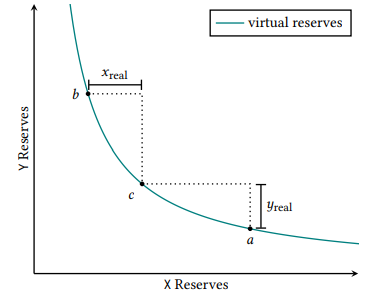
Figure: Simulation of virtual liquidity
A position needs to hold enough assets in reserve X to cover the price movements to its upper limit because price-rise would lead to depletion of X reserves. And in case of Y, it needs to holds enough Assets in the reserve Y to cover the downward price movement to its lower limit. In the above graph, the relationship is shown for a position on a range [pa,pb] and a current price pcЄ [pa,pb] and xreal and yreal represents the position’s real reserves.
What happens when the price exits the position range? The position’s liquidity is no longer active and does not earn fees. At this point, the reserve is composed of a single Asset as the reserves of the other asset must have been completely depleted. If the price again re-enters in the position, liquidity becomes active again. The real reserve of the position are calculated using
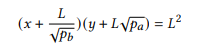
where, L is the amount of liquidity provided and is calculated as √k. The graphical representation of above equation is
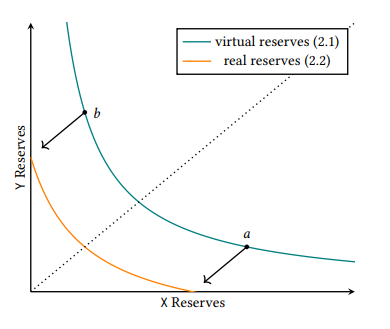
Figure: Real Reserves
This lets the market decide where to allocate liquidity and they can create as many as positions as can be fit into the price range. Rational Liquidity Providers can reduce cost of their capital by concentrating their liquidity in a narrow band around the current prices and then keep on adding/ removing tokens as the price moves.
Architectural Changes: Some of the changes that occurred from V1 and V2 to V3 were necessary to support concentrated liquidity positions while some are improvements in general. The improvements include (i) Multiple Pools Per Pair: Uniswap V3 allows multiple pool for each pair of token, with different swap fees while all the pools are created by the same factory contract and allows contract creation with three different fee categories 0.05%, 0.30% and 1% while it was 0.30% only in V1 and V2. In V3, additional fee structures can be implemented. (ii) Non-Fungible Liquidity: In V3, compounding of fees is not possible as fees are stored separately and are held as tokens in which fees are paid.
Governance: In Uniswap V3, UNI governance has more flexibility to change the fraction of the swap fees that is applicable on the protocols and also, it is able to implement additional layer of fee structures. It also has power to transfer ownership to another addresses.
Oracle: V3 does not require users of the oracle to track previous values of accumulator externally. In V3, it is possible to calculate arithmetic mean TWAP (Time-weighted Average Price) and geometric mean TWAP (V3 tracks the sum of log prices). It adds a liquidity accumulator which is tracked alongside the price accumulator that accumulates 1/L for each second.
Geometric mean TWAP can be calculated as between time period t1 and t2,
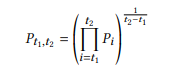
Implementing Concentrated Liquidity
- Ticks and Ranges: Ranges are specified as a range of signed integer tick indices: a lower tick (il) and a upper tick (iu). Ticks represent the prices at which the virtual liquidity of the contract can change. There is a tick at every price p, an integer power of 1.0001. Representing ticks by an integer index i, prices are given by,
p(i) = 1.0001i
When liquidity is added to a range, if one or both of the ticks are not already used as the upper or lower limits, in any of the existing positions, then the tick is initialized. Not all the ticks can be initialized. The pool is initialized with a parameter known as tick spacing so all the ticks that could be initialized should be divisible by tick spacing. If tick spacing is smaller than it allows for tighter and more precise ranges.
- Global State: The Global State of the contract includes seven storage variables relevant to swaps and liquidity positions.
Out of Liquidity and Price, only one changes at a time. Price changes when swapping within a tick and liquidity changes when crossing a tick or when minting or burning liquidity. L is calculated as x.y and P is calculated as y/x.
Current tick can be calculated on the basis of P . At any given point of time, the equation should be true is ic=[log1.0001P]
In Uniswap V3, fees are collected in the tokens themselves rather than liquidity. The global state of fees represents the total amount of fees that have been earned per unit of Virtual Liquidity L. The global state tracks the total accumulated uncollected protocol fees in each token and this can be collected by UNI governance.
Swapping in a Single Tick: When swapping one token for the other, the pool contract first compute the new P using formula P= y/L and to compute the amount of token0 or token1 to be send out using either of the two formulas: y=P .L or x=(1/P). L
Tick- Indexed State: Contract needs to store information about each tick in order to track the amount of net liquidity that should be added or removed when the tick is crossed, as well as to track the fees earned above or below that tick.
Position- Indexed State: Each Position structure tracks three values including liquidity, lower tick and upper tick to know the liquidity and uncollected fees position.


